- Greater Than Or Equal To In Microsoft Word Document
- Greater Than Or Equal To In Microsoft Word Free
- How To Write Greater Than Or Equal To In Word
- How To Put Greater Than Or Equal In Word
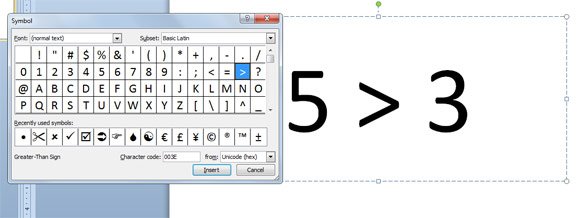
To get the ≥ symbol (the greater than or equal to) use the option key and the period key. To type the symbol (greater than) press shift and period key. On a PC keyboard it is just a little different. In Microsoft Word on PC it is quick to go to Insert, Advanced Symbol. How To Write Less than or equal to in Word How Insert Less than or equal to in Microsoft Word Type Less than or equal toThis Microsoft Word tutorial show.
OData (Open Data Protocol) is an OASIS standard that establishes best practices for designing RESTful APIs. One of the capabilities of OData is providing the ability to filter data using a standardized method across RESTful APIs, regardless if they are vendor provided or custom developed. Since Microsoft Flow's connectors are built-upon RESTful APIs, many of our connectors support the ability to filter datasets server-side using OData. Some of the benefits of using OData include reducing the amount of data you are bringing into your flow, thus reducing the need to loop through a record set to find values of interest.
In this blog post we are going to explore some popular OData filter expressions that you can use with some of our most popular connectors including SQL Server, Dynamics 365 and SharePoint Online.
Scenario #1: Get Rows from SQL Server and filter on Customer Name
We have the following Azure SQL database with a table that contains many work orders. From Microsoft Flow, we want to return only rows where the Customer Name is equal to 'Contoso'
Inside of Microsoft Flow, we can add a SQL Server – Get Rows action. After providing a Table name we also have the ability to provide a Filter Query . Inside this textbox we will provide a statement of CustomerName eq 'Contoso'. The breakdown of this syntax is we need to provide the name of the field in the source system (i.e. SQL Server), followed by an operator. In this case we want to use = which is represented as eq in OData. Don't use the = symbol otherwise you will get a runtime error. Lastly, we need to provide a value that we want to filter on. In this case we want to filter on Contoso. Since it is a string, we need to wrap it in single quotes ' '.
For the purposes of this blog post, we will wrap the results in HTML and send them via Office 365 Outlook connector so we can verify our results.
After the flow executes, our we will see our results rendered successfully and only records with a Customer Name of Contoso are displayed.

Scenario #2: Get Rows from SQL Server and filter on date
In this scenario we want to filter out older records and only retrieve records that have a Work Order Create Date that is less than 30 days old. To accomplish this we will also use a flow expression that will calculate the date, 30 days ago. We will then look for any records that have a Work Order Create Date that is greater than this date. The complete expression is: WorkOrderCreatedTime gt addDays(utcnow('yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ'),-30). In this scenario, WorkOrderCreatedTime is our source field, gt represents our 'greater than' operator and addDays(utcnow('yyyy-MM-ddTHH:mm:ssZ'),-30) will calculate a date of 30 days prior.
The results only include records that are less than 30 days old.

Scenario #3: List Records from Dynamics 365 using an AND clause
We will now move onto the Dynamics 365 connector where we can also use OData to filter out records. In this case we want to want to retrieve only records where the Account Name is Contoso Hospital AND the City is Phoenix .
To accomplish this we will use an AND clause that will let us join two statements. The first being our (Account) name being equal to 'Contoso Hospital' and secondly, our address1_city being equal to 'Phoenix'. Our complete statement is name eq 'Contoso Hospital' and address1_city eq 'Phoenix'.
When we execute our flow, we will see results only related to the Contoso Hospital in Phoenix.
Scenario #4: List Records from SharePoint Online that Starts With
In our final scenario, we are going to filter records from a custom SharePoint list. In this particular example, we have 4 records within a SharePoint List and we want to filter on all sites that start with the word 'Contoso' .
From a flow perspective, we will include the following OData query within our SharePoint action: startswith(Title,'Contoso') where Title is the name of the column that we want to filter on and Contoso is the value we want to the column to start with.
When our flow runs, we will discover that only the Site Names that beginthe word Contoso are included in our results.
Conclusion
In this blog post we covered 4 different OData queries across 3 different connectors including SQL Server, Dynamics 365 and SharePoint Online. While the syntax is a little different than what you are used to when using T-SQL, the power available to you unlocks new ways to filter your data in Microsoft Flow. Using OData to filter at the data source will reduce execution times as it reduces the need to loop through data sets in order to find specific records. So not only is this more efficient by sending smaller messages around, but it will also allow your flows to run faster.
For more examples of OData filter expressions, please check out the following Microsoft page.
Q: How do you type a unusual characters like “≥” (greater-than-or-equal-to) in Microsoft Word? (via Quora)

A: It’s easy!
Every electronic keyboard has a set of built-in computer codes for a given language’s most-commonly-used letters, numbers and punctuation. These are the symbols you see printed permanently on the tops of your keyboard’s keys.
But the entire universe of extended characters — virtually any letter, number, punctuation mark, mathematical symbol, etc., in almost any language — can be typed in by manually entering the correct, standardized computer code for that character, even if it’s not on the keyboard.
There are standardized codes to represent virtually any letter, number, punctuation, or symbol that you might want to generate. Some of the major code types include Unicode, ASCII (which includes decimal, hex, and octal versions), and HTML.
Greater Than Or Equal To In Microsoft Word Document
Which code you need to use depends on what equipment you’re using (e.g. Apple vs Microsoft), and what your intended medium is (printed document, web page, etc.)
In practice, there are two steps to finding the code you want:
First, in whatever document/webpage/file/etc. creation tool you’re using, open its Help system and search for extended characters. The info there will tell you how to enter unusual, not-on-the-keytops characters into whatever document or file you’re trying to create. For example, this Microsoft Help Page shows how to enter extended characters in Word/Office.
Next, following the directions on the above Help page, use any of the many available lookup tables (e.g. Unicode, ASCII, HTML…) to find the correct code for whatever character or symbol you’re your trying to create, and then simply type it in.
That’s all it takes!
For example here are the codes for GREATER-THAN OR EQUAL TO: ≥
ASCII: 0242
Greater Than Or Equal To In Microsoft Word Free
UNICODE: U+02265
HEX CODE: ≥
HTML CODE: ≥

HTML ENTITY: ≥
CSS CODE: 2265
Following the instruction on the Microsoft Help page for Office 365, you enter an ASCII character by pressing and holding down ALT while typing the character code on the numeric keypad. So, to insert ≥, press and hold down ALT while typing 0242 on the numeric keypad. Simple!
Permalink: https://wp.me/paaiox-5L
How To Write Greater Than Or Equal To In Word
Ask me anything! Click the CONTACT link on any page.
How To Put Greater Than Or Equal In Word
Share this item via the links below: